Cytogenetic Technologists
Overview

Introduction
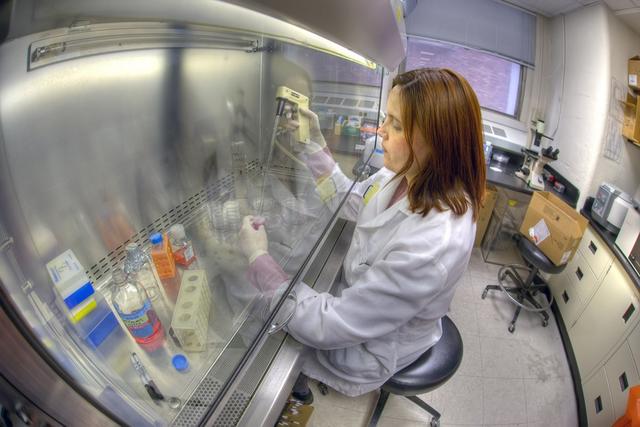
Cytogenetic technologists research chromosomes in biological samples to analyze for genetic diseases and disorders. They use microscopes and various medical imaging equipment to study samples such as bodily fluids, bone marrow, blood, tissue, and other genetic material from patients. Cytogenetic technologists maintain records and write reports of their studies. They consult with other laboratory workers and pathologists. Most technologists work in private medical laboratories or in the laboratories of hospitals or research facilitie...
Quick Facts
Median Salary
Employment Prospects
Minimum Education Level
Experience
Skills
Personality Traits
Earnings
Salaries for cytogenetic technologists vary based on education, work experience, and type of employer. ZipRecruiter.com reported that in November 2024, the median annual salary for cytogenetic technologists was $70,062. Salaries ranged from $49,000 or less to $119,500 or higher.
Medical and clinical laboratory technicians, including cytogenetic technologists, earned a median annual salar...
Work Environment
Cytogenetic technologists work in climate-controlled, well-lighted laboratories, spending much of their time using microscopes, medical imaging equipment, and computers. The job requires intense concentration for accuracy or exactness. Technologists must follow laboratory procedures and protocols. The job can be stressful at times, especially when working under deadline pressure. Cytogenetic te...
Outlook
Employment of clinical laboratory technologists and technicians (including cytogenetic technologists) is projected to grow 5 percent, about as fast as the average for all careers, through 2033, according to the U.S. Department of Labor.
Cytogenetic technologists will continue to be needed by medical and diagnostic laboratories and research facilities to identify genetic disorders and dis...