Textile Manufacturing Workers
Overview

Introduction
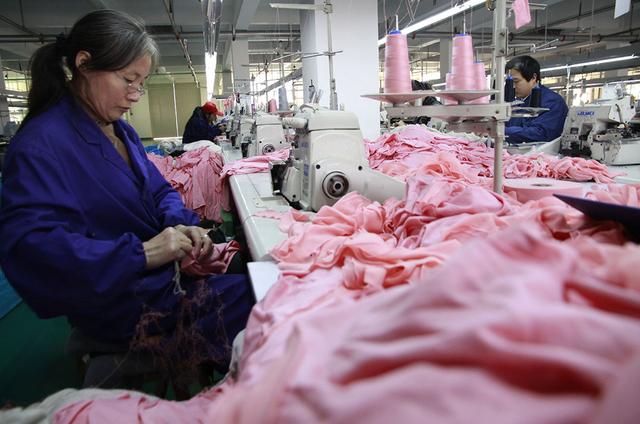
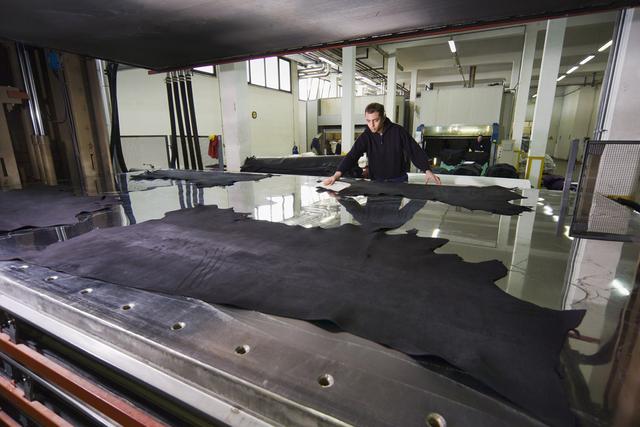
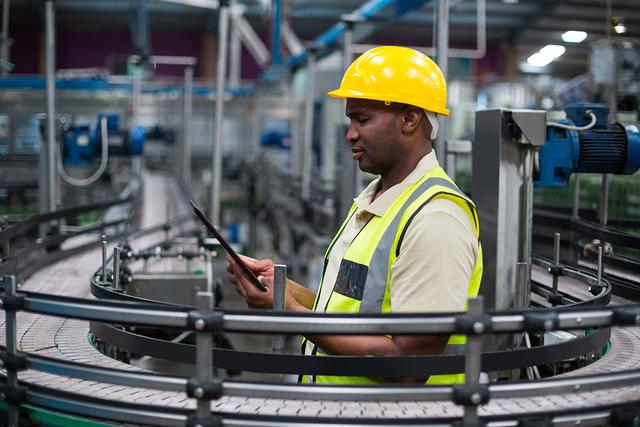
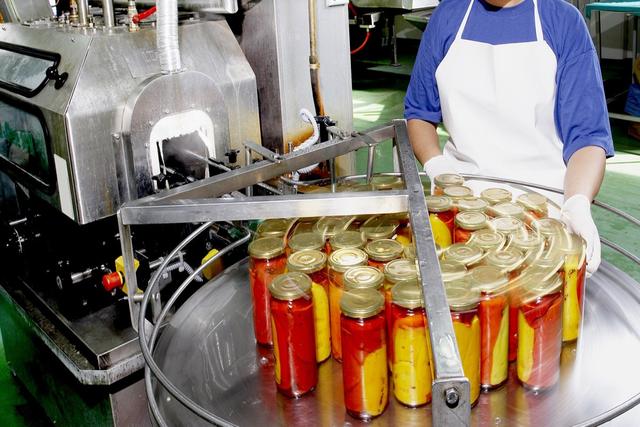
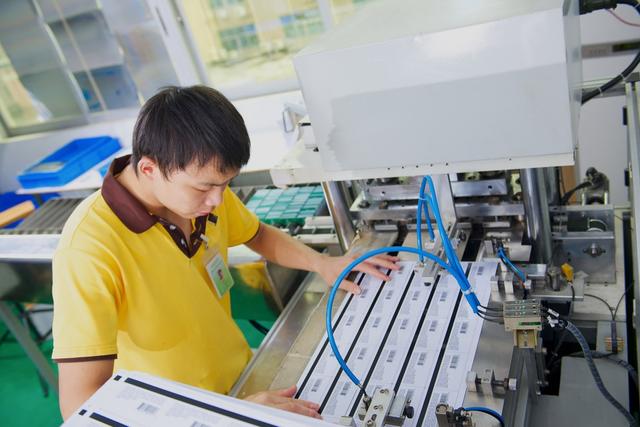
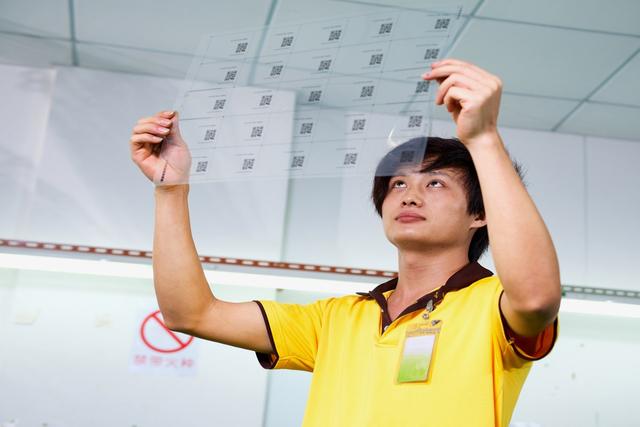
Textile manufacturing workers prepare natural and synthetic fibers for spinning into yarn and manufacture yarn into textile products that are used in clothing, in household goods, and for many industrial purposes. Among the processes that these workers perform are cleaning, carding, combing, and spinning fibers; weaving, knitting, or bonding yarns and threads into textiles; and dyeing and finishing fabrics. There are approximately 111,300 workers employed in apparel manufacturing and 18,060 textile, apparel, and furnishings workers,...
Quick Facts
Median Salary
Employment Prospects
Minimum Education Level
Experience
Skills
Personality Traits
Earnings
Earnings of textile industry workers vary depending on the type of plant where they are employed and the workers job responsibilities, the shift they work, and seniority. Workers at plants located in the North tend to be paid more than those in the South.
In May 2019, textile knitting and weaving machine setters, operators, and tenders earned median wages of $11.75 an hour (or $26,520 an...
Work Environment
Work areas in modern textile plants are largely clean, well-lighted, air-conditioned, and humidity controlled. Older facilities may be less comfortable, with more fibers or fumes in the air, requiring some workers to wear protective glasses or masks. Some machines can be very noisy, and workers near them must wear ear protectors. Workers also must stay alert and use caution when working around ...
Outlook
The U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) predicts a steep decline in employment for this field through 2029, even as the demand for textile products increases. Changes in the textile industry will account for much of this decline. Factories are reorganizing production operations for greater efficiency and installing equipment that relies on more highly automated and computerized machines and processe...